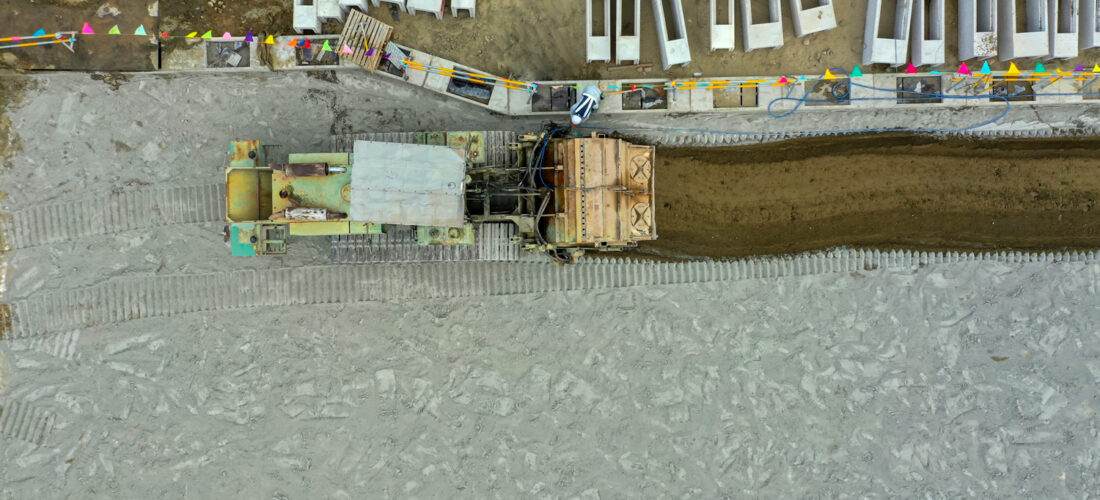

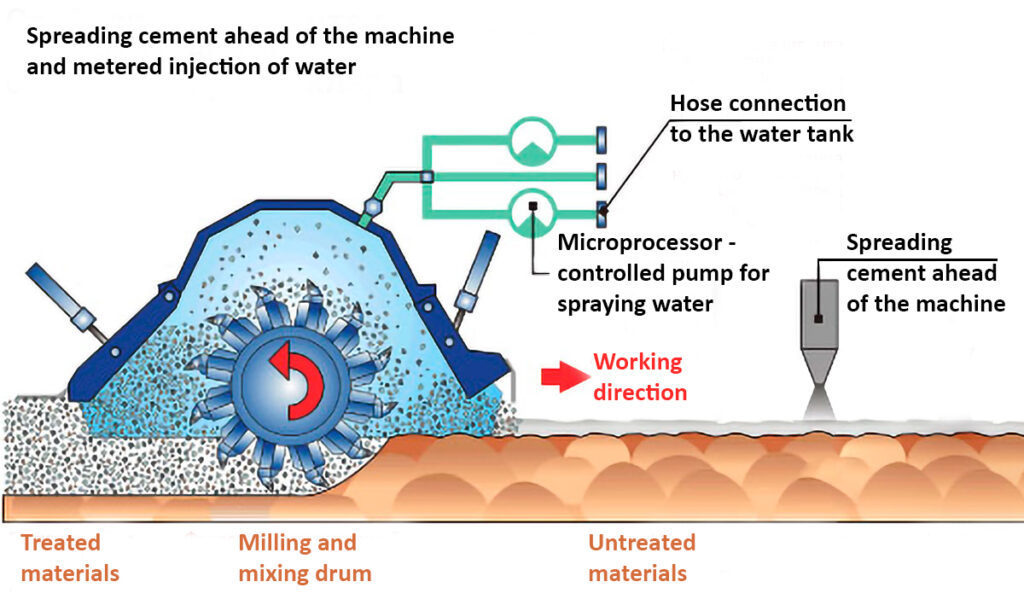
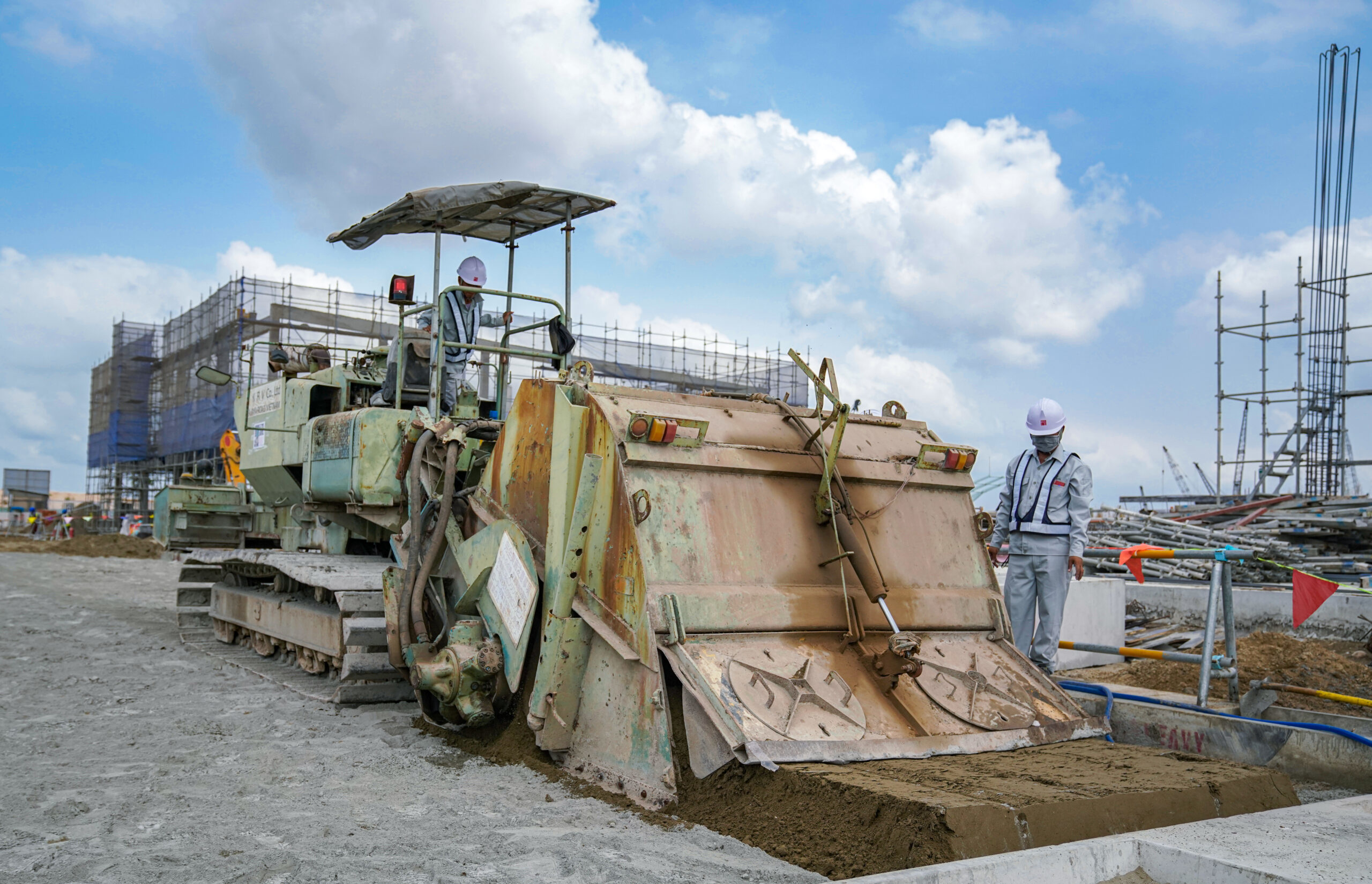
Soil stabilization is a construction method in which additives, such as cement & lime, are spread on the surface of weak subgrade soil to be mixed with it for the purpose of improving its bearing capacity.
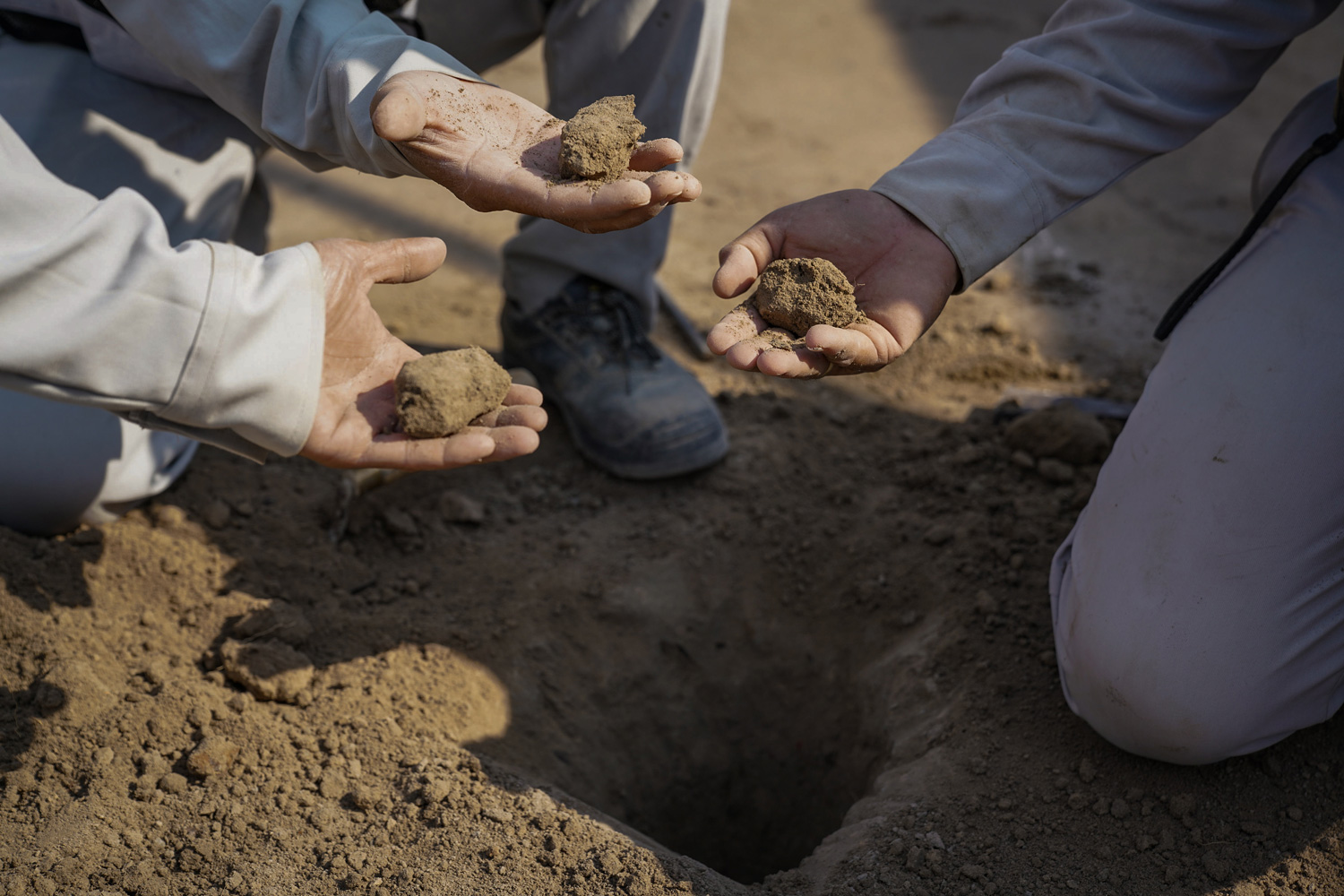

“By mixing cement or liming material with soft ground, the bearing capacity of the ground is improved.“
Benefits of Soil Stabilization
Technical Benefits:
- Treatment with lime and/or cement allows production of a long lasting and stable material comparable to those of graded aggregates.
- Excellent Improvement of ground conditions such as CBR, E-modulus, modulus of ground reaction, ground drainage, soil properties & etc.
- Hard wearing, with greater stiffness and strength they provide excellent performance within the construction process and have become widely recognized as a strong alternative to typical construction methods.
Financial Benefits:
The recycling and re-use of in-situ materials gives significant savings:
- Minimize the stripping and removal to landfill of material along with their associated transport costs.
- Save on the import of aggregates.
- The duration of the works are shorter, giving further savings to the contract program.
Environmental Benefits:
There are significant environmental benefits of soil stabilization in comparison to traditional construction methods including:
- Energy savings by reducing the transport of materials (this also reduces the indirect effects including nuisance to the public).
- Minimizing the use of aggregate resources that are by-products of the energy industry.
Comparison with Traditional Design
- Hot-mixed Asphalt Pavement:
For Hot-mixed Asphalt Pavement, the Soil Stabilization will replace for the Sub-base layer. The thickness of Soil Stabilization layer is from 200mm to 350mm commonly. The Base Course layer may be also
replaced by the Soil Stabilization with a higher content of additive cement.
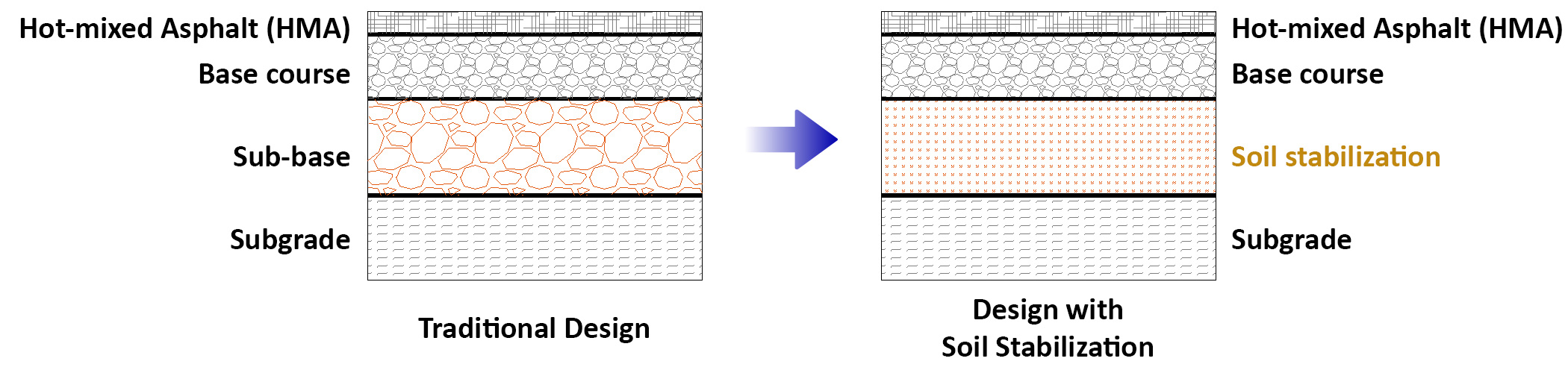
- Cement Concrete Pavement:
For Cement Concrete Pavement, the Soil Stabilization will replace for the Base course layer. The thickness of Soil Stabilization layer is from 200mm to 350mm commonly.
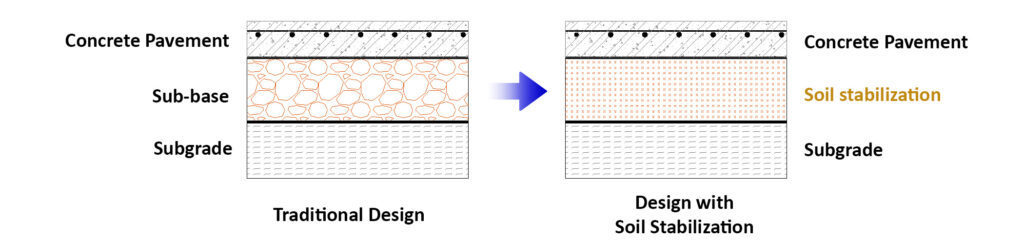
Benefits of Soil Stabilization vs Traditional Crushed Stone
- Minimize tripping, excavation & transport:
- Save the cost of tripping, excavation along with their associated transport
- Save the total construction time
- Save the cost of aggregate materials
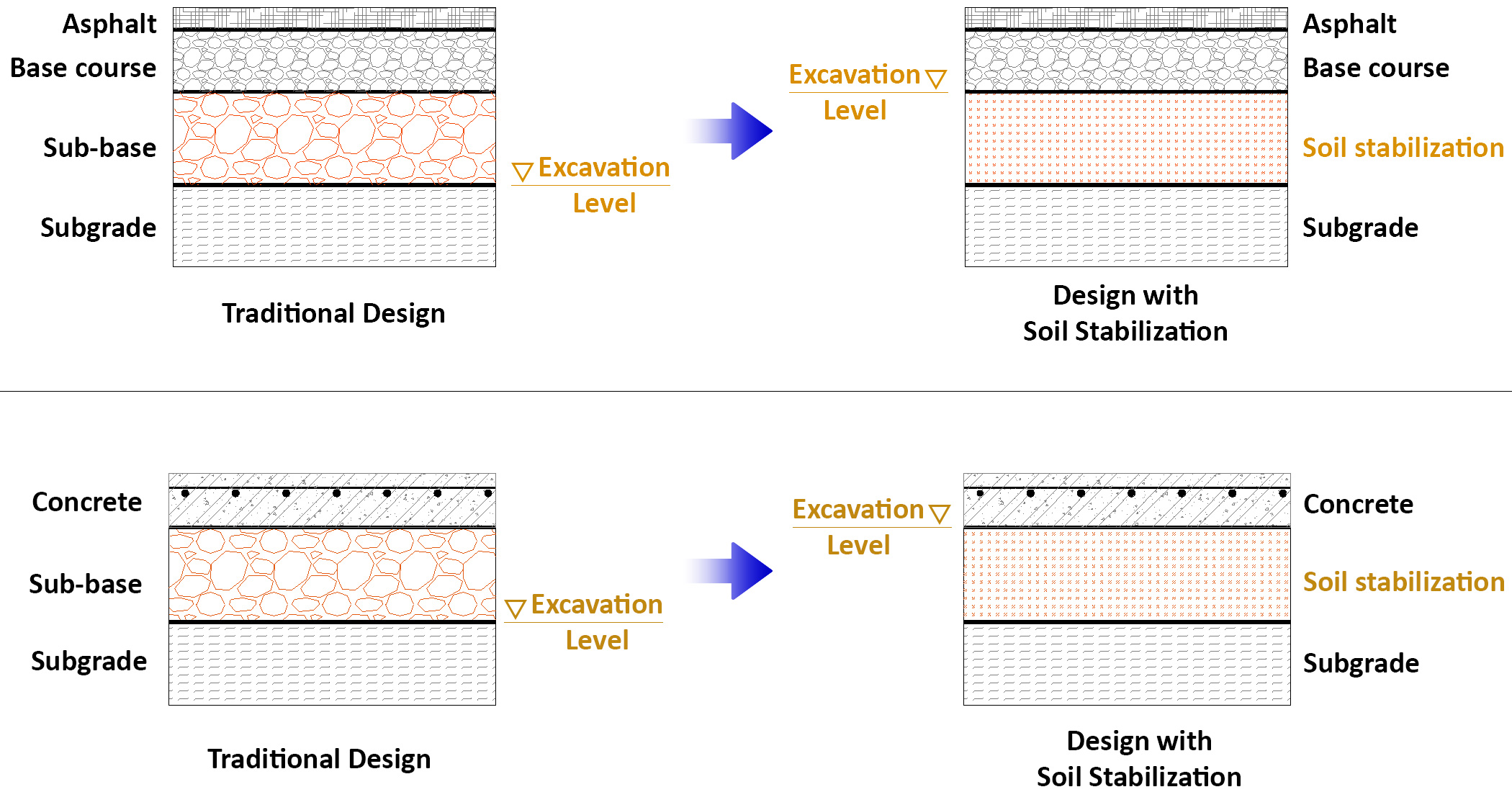
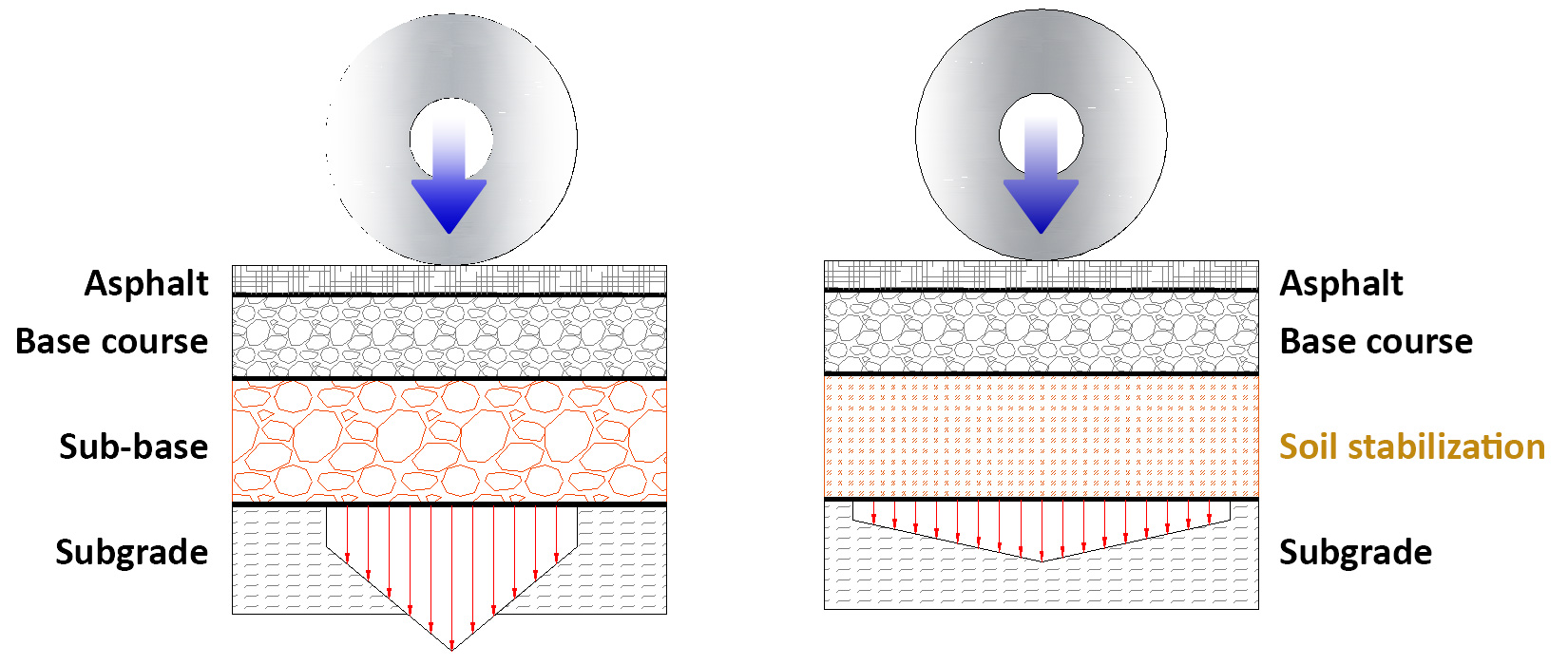
- Minimize rutting or fatigue cracking:
- Distribute the loads to the below foundation for Flexible Pavement
- Provide uniform stable support for Rigid Pavement
- Minimize cost of temporary construction road:
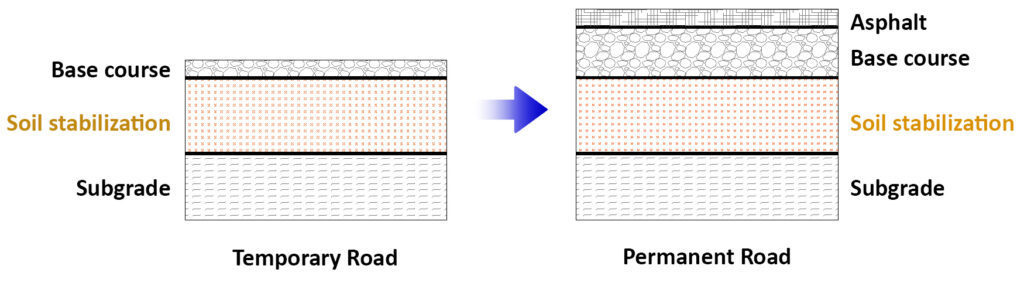
- Remove temporary base course
- Contruct remain layer for Asphalt pavement or Concrete pavement
EVALUATION METHOD
- Design
- Unconfined Compression Strength (UCC) to identify the suitable cement content for the Soil Stabilization. Target UCC for each Stabilization Method as following (kgf/cm2):
| Stabilization method | Classification of Pavement | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| General traffic | Light traffic | |||
| Base | Sub-base | Base | Sub-base | |
| Cement | 30 | 10 | 25 | – (*) |
| Lime | 10 | 7 | 7 | – (*) |
(*) No requirements, as the aim of stabilization is increase the CBR value & lower the PI value, so that sub-base materials conform to requirements.
- Modified CBR test to identify the optimum cement content in case of considering the improvement of the CBR value.
- Other tests if desired such as Specific gravity, LL, PL, PI, etc. of the soil & the Stabilized Soil.
- Construction Quality Control:
- MDT, FDT to make sure the suitability of the compaction procedure.
- Plate Bearing test to get the values of E-modulus, modulus of ground reaction (k) or CBR, etc. so that the Soil Stabilization has been proved to satisfy the designatory requirements.




Post a Comment